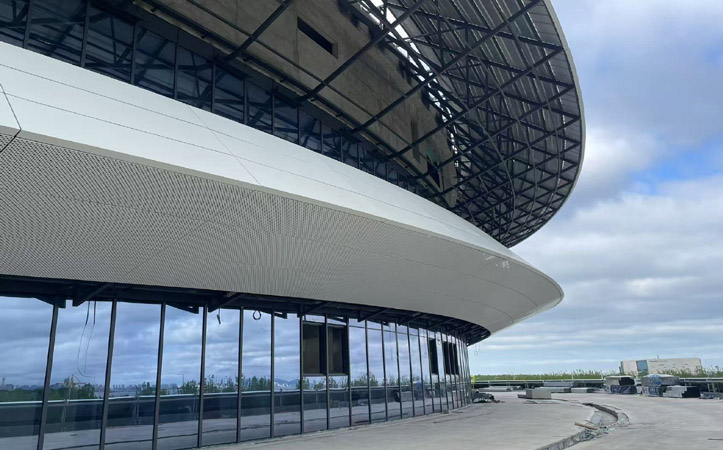
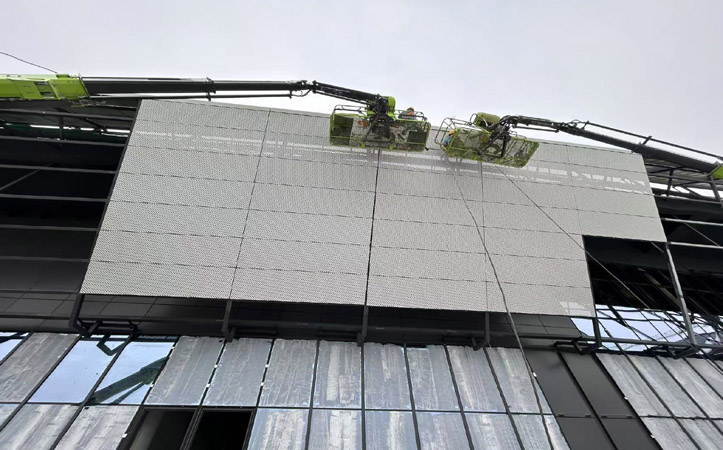
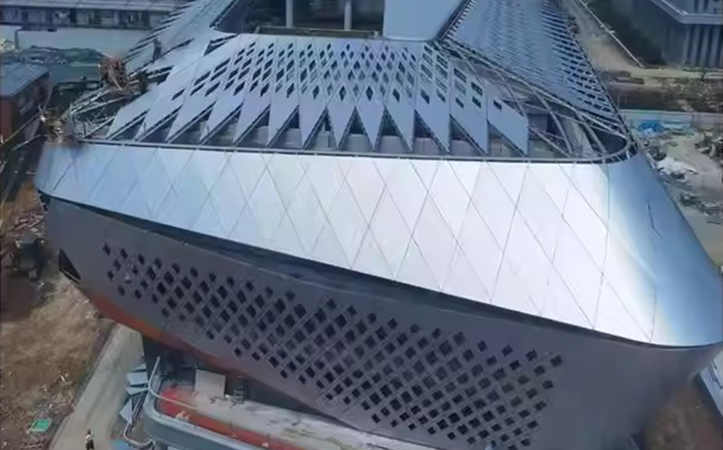
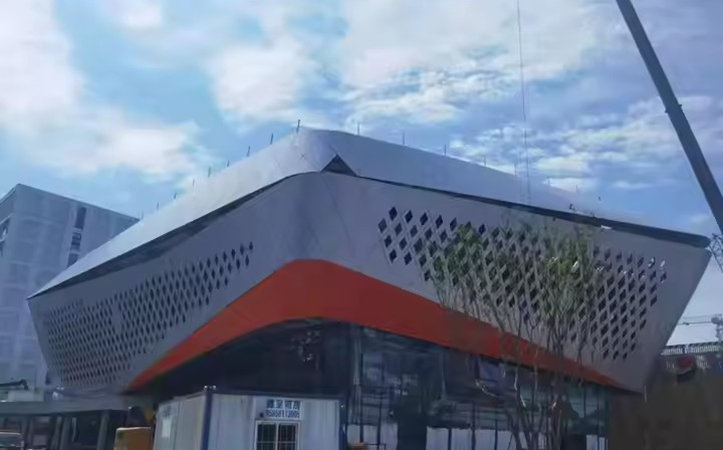
What is Perforated Sheet Metal?
Perforated metal involves sheet material that has been stamped, punched, or crafted to form a series of holes, slots, or ornamental shapes. This manufacturing technique can utilize several types of metals, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and titanium. Beyond boosting the structural appearance of metal, perforating offers practical advantages like enhanced protection and noise mitigation.
Choosing which metal to perforate depends on criteria such as size, gauge thickness, material type, and the purpose of use. The array of possible shapes is remarkably flexible, featuring choices like circular holes, square cutouts, slotted patterns, hexagonal designs, and more.
How Perforated Sheet Metals are Made?
Perforation, once a highly labor-intensive process, has now been modernized and automated to meet contemporary standards in the metal fabrication industry. The three prevalent techniques for producing perforated panels—punch press, rotary pin, and laser cutting—form the foundation of modern perforated sheet metal manufacturing. These processes are essential for enabling high-volume, precise, and customizable production of perforated metal sheets used across a wide variety of industries, including architecture, filtration, acoustics, and automotive engineering.
Each of these perforating methods offers distinct advantages for creating various configurations, shapes, and patterns, catering to diverse end-use requirements and performance specifications.
How Perforated Metals are Made Sheet Metal
The production of perforated metals starts with thin, flat sheet metal made from materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel, brass, copper, and galvanized steel. These metal sheets can be cut, bent, shaped, or otherwise fabricated depending on project needs. Metal thickness is measured in gauges, with higher gauge numbers indicating thinner metals. Material selection impacts durability, corrosion resistance, appearance, and suitability for specific environments, such as outdoor architectural facades or industrial filtration systems.
Related Products
- Address
No.3 Beishang New City, GongShu District, Hangzhou China
-
Phone
+86-18072735884
-
Landline
+86-571-88688170

 English
English